Understanding ECG Monitor Waveforms
Although they are not to be used for diagnosis, your handheld portable monitor is an excellent tool to be used in conjunction with your health care profession. It should allow you to have a deeper understanding of your heart health. Here is an introduction on the ECG rhythms that might be recorded.
Normal sinus rhythm
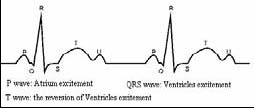
In sinus conditions, SA node paces the heart with a regular rate and the normal rhythm. P wave is normal and each one is followed by a QRS wave. P-R interval: 0.12 ~ 0.20s; QRS wave: 0.06 ~ 0.10s; no ectopic ECG activity. The display of "no apparent irregularity" may be regarded as Normal sinus rhythm.
The pulse rate for adult is in the range of 60 to 100 times per minute with less than 10% variation. For pulse rate under 60 bpm, it is sinus bradycardia; for pulse rate over 100 bpm, it is sinus tachycardia; for over 10% variation, it is sinus arrhythmia. The normal heart rate varies with age; for newborn, the rate can go up to 150 bpm.
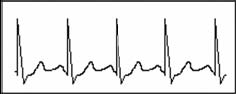
Symptom: Sinus rhythm, heart rate: 60~100bpm
Indication: Normal
Abnormal ECG rhythms
Tachycardia
Tachycardia typically refers to a heart rate that exceeds the normal range for a resting heart rate (heart rate in an inactive or sleeping individual). It can be dangerous depending on the speed and type of rhythm. For an adult (greater than 15 years old), the threshold is 100 bpm. The display of "fast beat" may be doubted as Tachycardia. There are different types of tachycardia and they are classified into narrow and wide complex based on the QRS complex. Examples are: sinus tachycardia, junctional tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia.
Symptom: Heart rate > 100bpm
Indication: It may occur with the normal people who have these physiology conditions: rage, fatigue, smoking, drinking too much wine, excessive coffee and strong tea, etc.
Pathology: Anemia, Hyperthyroidism, blood hypoxia, myocarditis, hypokalemia, fever, influence of some medication (such as atropine, epinephrine etc.).
Suggestion: If it belongs to pathology condition, please go to hospital.
Bradycardia
Bradycardia is the resting heart rate of under 60 beats per minute, though it is seldom symptomatic until the rate drops below 50 beat/min. It may cause cardiac arrest in some patients, because those with bradycardia may not be pumping enough oxygen to their heart. It sometimes results in fainting, shortness of breath, and if severe enough, death. The display of "slow beat" may be suspected Bradycardia.
Trained athletes or young healthy individuals may also have a slow resting heart rate. Resting bradycardia is often considered normal if the individual has no other symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, chest discomfort, palpitations or shortness of breath associated with it.
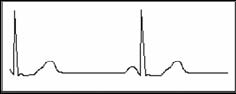
Symptom: heart rate < 60bpm
Indication: It occurs when healthy people fall asleep, and it can be found in athlete (or those who love doing sports frequently), old people, or vagus excitement person.
Pathology: Sick sinus syndrome, Ischemic heart disease, Cardiomyopathy, intracranial hypertension, increased hypokalemia, Low temperature, period of convalescence of acute infectious disease or after use some medicines such as digitalis.
Suggestion: If it belongs to the pathology condition, please see a doctor.
Premature beat
Premature beats (contractions) are beats that occur earlier than expected and briefly interrupt the normal heart rhythm. Premature beats are the most common cause of an irregular heartbeat. Although they tend to be more common in people with heart disease, almost everyone experiences them at least occasionally. Premature beats often cause a sensation of a "skipped beat" or "flip-flop." What are really felt are not the premature beats themselves but rather the forceful beat that follows the pause after the premature beat. During the pause, the heart has more time to fill with blood making the next beat more forceful. Premature beats are sometimes but not always associated with other arrhythmias.
The phenomena of a premature beat between two heart beats is called inserting premature beat
Premature beats may originate from anywhere in the heart. The most common form of premature beat seen in daily practice is a premature contraction originating in the ventricle (PVC =premature ventricular contraction). Premature contractions in the atria (PAC) are also rather common.
The display of "early beat" may be suspected Premature beat.
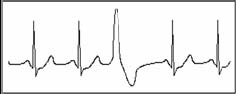
Symptom: The heart beat is arrhythmic, it occurs as the phenomenon that the heart suddenly beats and then stops for a while. Some people have palpitation or have no symptom.
Indication: The premature beat can be found occasionally in healthy people, with no distinct symptom or sometimes with palpitation. This may be caused by fatigue, anxiety, insomnia, smoking too much, or drinking too much wine, coffee, strong tea etc. It can be recovered without treatment. However, if premature beat occurs frequently, continuously or in multi-focus, it will indicate functional cardiovascular disease. please see a doctor as soon as possible.
Suggestion: The character of premature beat needs professional to confirm, so please save the temporal figure in time. When seeing a doctor , you can recall it to doctor to judge the character of premature (Premature Atrial Contraction, Premature Nodal Contraction, Premature Ventricular Contraction or multi-focus premature beat ) and help cure.
General characteristics: Normal heart beat is followed by a premature beat.
Bigeminy
It is a type of PVC in which a normal beat is coupled with a premature beat.
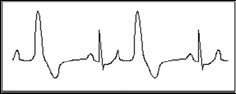
Indication: PVC occurs frequently.
Suggestion: Please see a doctor.
Trigeminy
It is a type of PVC in which two normal beats are coupled with a premature beat.
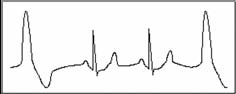
Indication: PVC occurs frequently.
Suggestion: Please see a doctor.
Short run of tachycardia
PVC (Premature Ventricular Contraction) occurs more than 3 times continuously.
Symptom: PVC occurs More than 3 times continuously. The heart beat is fast and regularly, but starts and stops suddenly. According to the different of active original position, it can be divided into: Short Run, SVE Short Run (Needing professional to judge).
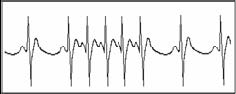
�Short Run
It is caused by Premature Atrial Contraction or Nodal Premature Beat, frequency>180bpm.
Indication: Most commonly found in healthy people, it causes by deep respiration, tachypnea, positional changes, swallow, rage etc. It also appears in functional cardiac disease, such as Wolff - Parkinson-White Syndrome, rheumatic heart disease, coronary heart disease, Cardiomyopathy, Congenital heart disease, medicinal reaction ( digitalis toxicosis) etc.
Suggestion: If it occurs time after time, please see a doctor as soon as possible.
�Ventricular Tachycardia
Caused by Premature Ventricular Contraction, Heart Rate >140bpm.
Indication: Most commonly found in heart disease patient, it can cause ventricle fibrillation if it's serious, so the tester needs to see a doctor immediately.
Suggestion: The character of short run needs professional to confirm, so please save the temporal figure in time. And you can provide it to doctor as a reference.
Missed beats
If the interval of heartbeats is twice the interval of prevenient heartbeats (on average) and is not followed by PVC (Premature Ventricular Contraction), it detected as missed beat. The display of "missing beat" may be doubted as Missed beats.
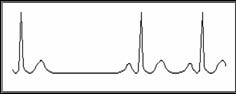
Symptom: Arrhythmia, a long time interval.
Indication: May be the conduction system of heart blocks, it often occurs in functional cardiovascular disease, Hyperthyroidism and myocardial disease. But sometimes it occurs in health people whose vagus is excited excessively(such as trained athlete).
Suggestion: Save the figure and see a doctor.
Ventricular arrest
No heartbeat is recorded for 4 or more seconds. The display of "beat pause" may be doubted as Ventricular arrest.

Symptom: Feel that the heart stops beating for several seconds.
Indication: Sinus arrest, or occurs in health people whose vagus is excited excessively, such as bellyache, sadness, sleeping etc. It also may occur in patients who suffer from functional cardiovascular disease, such as myocarditis, myocardial infarctions, cardiac pathological changes, etc.
Suggestion: Save the figure and see a doctor.
If the user has heart attack symptoms such as chest tightness, asphyxia, or amaurosis etc, please see a doctor immediately.
|
|
|